Time Intelligence Functions
The image below shows the output of each Time Intelligence Function when we pass as parameter a column ‘Date’[Date] containing two dates: 2017-12-01 and 2017-12-02.
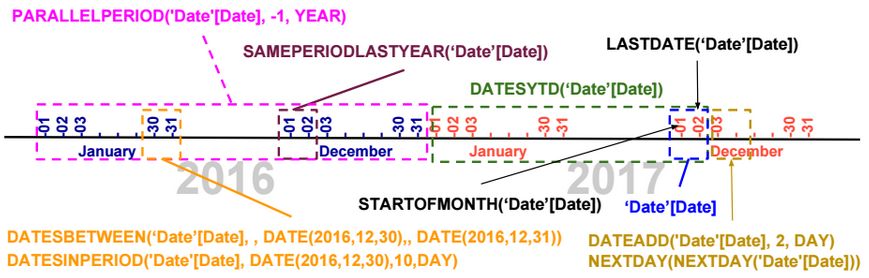
Using the CALCULATE function, we can evaluate a measure based on the result of a Time Intelligence function.
CALCULATE([TotalSales], DATESYTD(‘Date’[Date]))
Last Non Blank Function
LastNonBlank is a DAX function that returns the last value of a column for which an expression is not blank.
The DAX expression below returns the last date the measure Stock is not blank.
LASTNONBLANK(‘Date'[Date], [Stock])
Calendar Functions
To generate a calendar, we can use the following functions: CALENDAR, CALENDARAUTO.
Table Functions
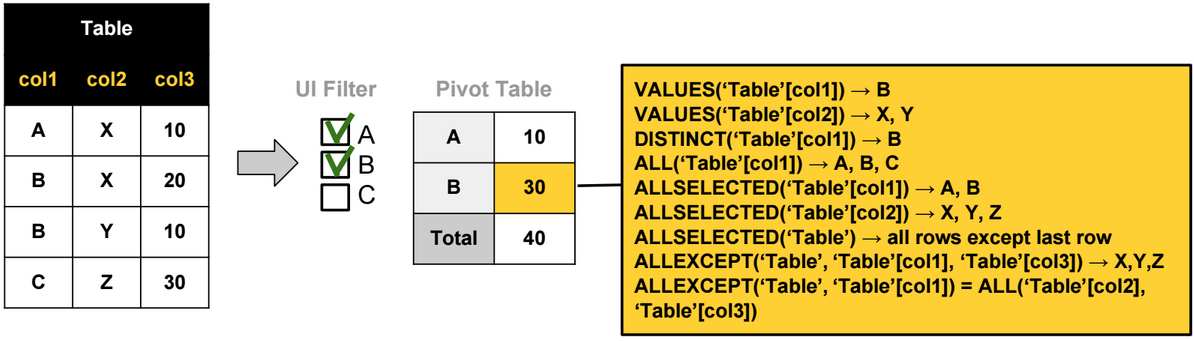
The most used Table functions are:
ALL: Ignores any filters that might have been applied on a table or a column.
ALLSELECTED: Ignores any filters that might have been applied on a table or a column, but retains explicit filters (like Excel slicers). (In reality, this function removes all filter contexts generated by context transitions).
DISTINCT: Returns a one-column table that contains the distinct values from the specified column
VALUES: Returns a one-column table that contains the distinct values from the specified table or column.
ALLEXCEPT: Ignores any filters that might have been applied except on the specified columns. For example ALLEXCEPT(‘Table’, Table’[col1]) is equivalent to ALL(‘Table’[col2],‘Table ’[col3]).
ALLNOBLANKROW: Ignores any filters that might have been applied on a table or a column, returns all rows but the blank row, or all distinct values of a column but the blank row.
Path Functions
Path functions are usually used when defining parent-child hierarchies. Below an example that shows how we can use these functions to create a parent-child hierarchy.
In the table below, we have a parent-child relationship based on two columns: Id and ParentId.

The 5 calculated columns on the right are defined using the following DAX expressions:
|
Calculated Column |
DAX Expression |
|
Path |
=PATH([Id],[ParentId]) |
|
Depth |
=PATHLENGTH([Path]) |
|
Level1 |
=IF([Depth] >=1, LOOKUPVALUE([Name],[Id], VALUE(PATHITEM([Path],1,1))), [Name]) |
|
Level2 |
=IF([Depth] >=2, LOOKUPVALUE([Name],[Id], VALUE(PATHITEM([Path],2,1))), [Name]) |
|
Level3 |
=IF([Depth] >=3, LOOKUPVALUE([Name],[Id], VALUE(PATHITEM([Path],3,1))), [Name]) |
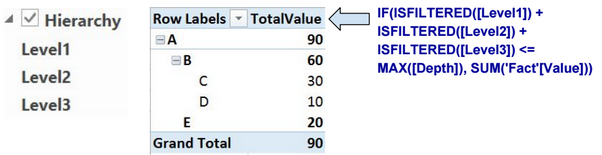
We use the columns Level1, Level2, and Level3 to define the parent-child hierarchy.
LookUpValue Function
LookupValue function retrieves a lookup value from a lookup table.
Count Functions
COUNT: Count numeric values.
COUNTA: Count rows different than blank.
COUNTBLANK: Count rows equal to blank.
COUNTROWS: COUNTA + COUNTBLANK.
DISTINCTCOUNT: Distinct count including Blank values.
Other Functions
ISEMPTY
IFERROR, ISERROR
LEN, LEFT, RIGHT, SEARCH, SUBSTITUTE, REPLACE, FORMAT
DIVIDE
SWITCH
ISBLANK, ISTEXT, ISNONTEXT, ISNUMBER
CONCATENATEX
RANKX
ISFILTERED, ISCROSSFILTERED
HASONEVALUE
FLOOR, TRUNC, ROUNDDOWN, CEILING, MROUND, ROUNDUP
YEAR, MONTH, DAY
More details about these functions can be found here: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee634396.aspx